What is a cardiac stent? Everything you need to know.
By Dr. Rishabh Mathur in Cardiology Interventional Cardiology
Sep 24, 2020
As cardiovascular disease (Heart attack) has emerged as the No. 1 killer in society so that use of cardiac stents in medical practice. Here is some important information you need to know about cardiac stents.
What is a stent and what is its function?
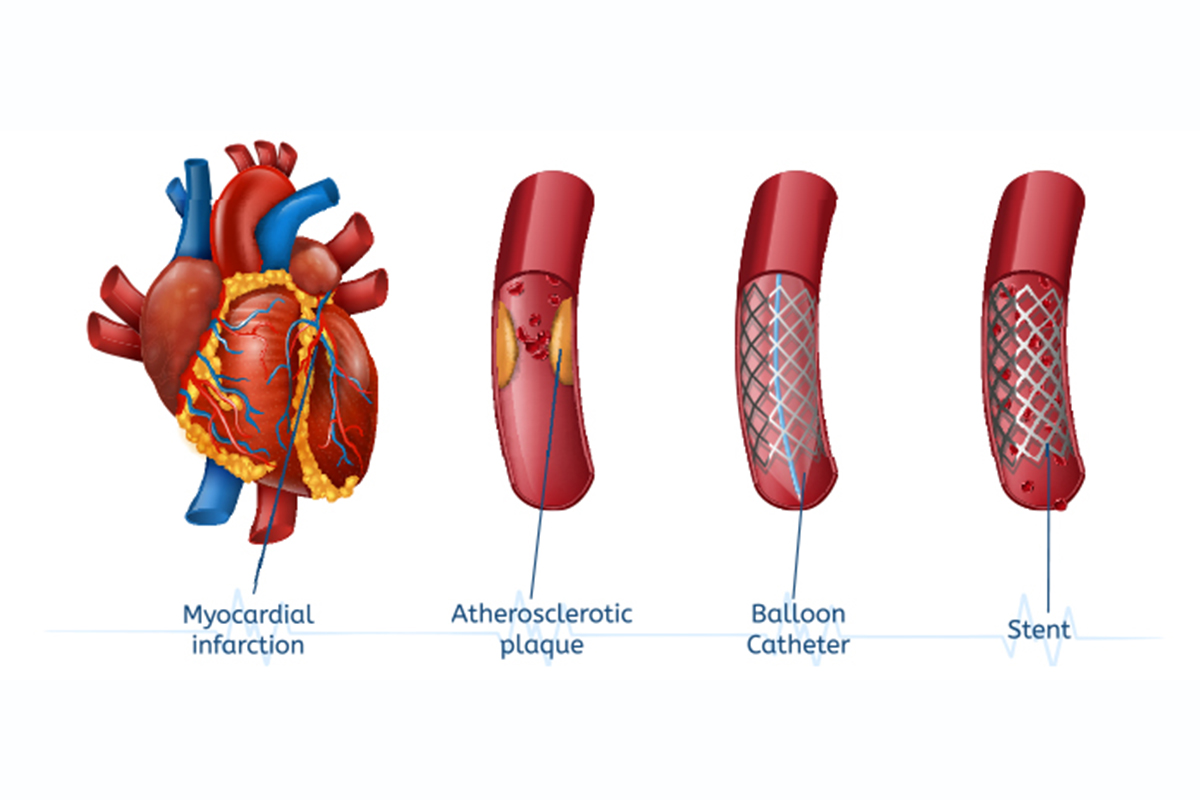
A stent is a small mesh tube made of either stainless steel or cobalt-chromium alloys that is placed by a catheter into a narrowed (blocked) coronary artery supplying blood to the heart. The stent helps enlarge a segment of the artery to improve blood flow, which should reduce or eliminate symptoms of chest pain. Stent technology is continually developing so we now use stents coated with medication which helps prevent the stent from clogging and narrowing (a process called restenosis).
Who needs a stent?
Stents are used to reduce symptoms in patients with blockages in the coronary artery, who suffer chest pain/tightness or shortness of breath that might be experienced with exercise or during periods of strong emotions. Stents may be used instead of bypass surgery in some selected patients. Diabetic patients with multiple coronary blockages may do better with bypass surgery.
How is a cardiac stent inserted?
Your doctor can insert a cardiac stent under local anesthesia. First, they will make a small incision in your groin, arm, or neck. Then, they will insert a catheter with a stent and balloon on the tip.
They will use special dyes and monitors to guide the catheter through your blood vessels to the narrowed or blocked coronary artery. When they reach the narrowed or blocked area, They will inflate the balloon. This will expand the stent and stretch the artery, allowing for increased blood flow. Finally, your doctor will deflate the balloon, remove the catheter, and leave the stent behind.
What happens after the procedure?
Recovery from an angioplasty and stent implantation is usually fast. Most patients can resume normal activities 24 hours after the procedure. Some people experience bruising, which will disappear in a few days.
Due to a heightened risk of clotting after stenting, treatment with Aspirin and antiplatelet drugs (also called anti-clotting drugs) is required for at least one year. Make sure you understand the dosage and duration of the medications as detailed by your doctor. Do not stop these medications without consulting Your cardiologist.
What are the benefits of cardiac stenting?
For many people, stenting has a positive impact on quality of life. The combination of angioplasty and stenting can be a lifesaver, especially when performed right after a heart attack.
It can substantially improve your blood flow and prevent further damage to your heart muscle. It can also improve symptoms of heart disease, such as chest pain (angina) and shortness of breath,. In many cases, you will feel the benefits immediately.
What are the risks and complications of cardiac stenting?
As with many medical procedures, you may experience an allergic reaction to the medications or materials used for angioplasty and stenting. Angioplasty can also cause bleeding, damage to your blood vessels or heart, or irregular heartbeat. Other potential but rare complications include heart attack, kidney failure, and stroke.