Breast Cancer- Symptoms, Causes, Stages & Treatment
By Dr. Piyusha Kulshrestha in Cancer
Nov 22, 2022
Breast Cancer develops when the cells in your breast multiply and expand out of control, forming a lump of tissue called a tumour. In females, breast cancer is the most prevalent invasive malignancy, being the primary contributor to female cancer mortalities.
Breast cancer is commonly diagnosed in women over 50, although it can strike anybody at any age. Let’s understand its various aspects.
What are the Symptoms of Breast Cancer?
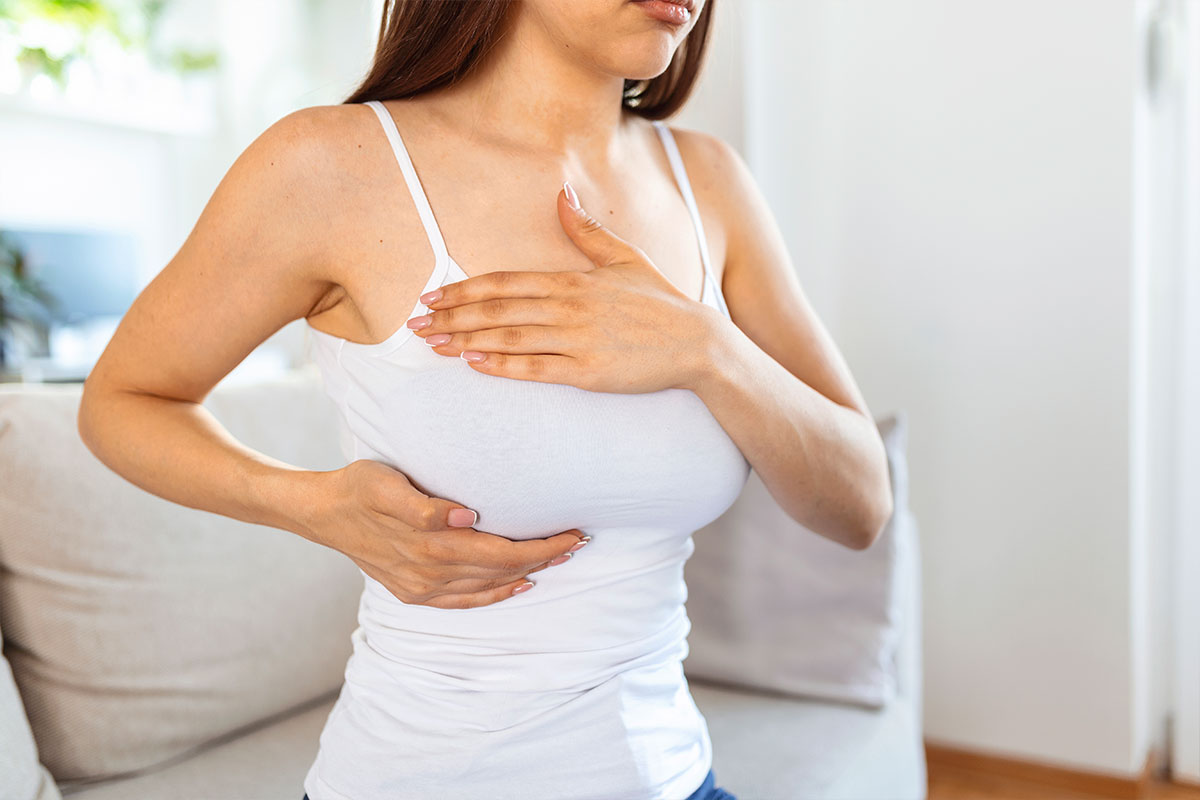
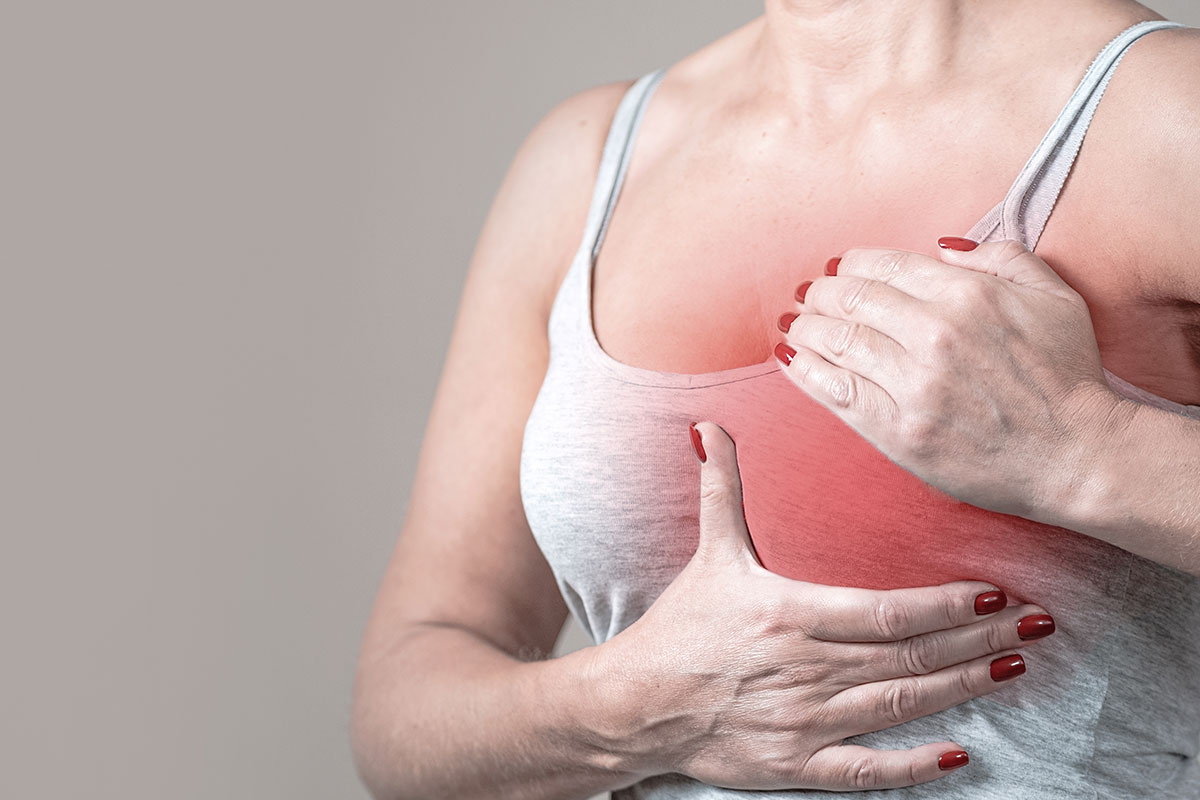
The clinical signs indicating breast cancer might differ from person to person. The first sign of breast cancer is typically a swollen patch of tissue in the breast, a lump in the breast, or a bulge in the armpit.
Other signs and symptoms include:
- A tumour or lump that lasts the entire menstrual cycle in your breast, the area around it, or under your arm.
- During your menstrual cycle, it causes discomfort or slight pain in the breast or armpit.
- Secretion from a nipple, which may contain blood.
- A marble-like firm region beneath your skin.
- A rash on one nipple or surrounding it.
- The skin on the breast or nipple is flaking, peeling or scaling.
Why does breast cancer happen? – CAUSES
When abnormal cells in the breast proliferate and spread, breast cancer develops. Cells in your breast can spread (metastasize) to your lymph nodes or other regions of your body. The precise reason this process starts in the first place is unknown to experts.
According to research, there are several factors that might raise your risk of having breast cancer. These consist of the following:
- As you age, your chances of breast cancer rise. Your risk of acquiring breast cancer increases if you are 55 or older.
- Breast cancer is more likely to develop at some time in your life if your parents, siblings, or other close relatives have already been diagnosed.
- High chance of breast cancer in the other breast if you have already had breast cancer in one.
- It is highly likely to get breast cancer if you’ve previously undergone radiation therapy, particularly for the head, neck, or chest.
- People who utilise hormone replacement treatment (HRT) have a greater chance of developing breast cancer.
Stages of Breast Cancer
How much cancer has already spread in your body is described by its stage. It aids in determining the severity of the malignancy and the most effective course of treatment. Several variables determine this, including the size and location of the tumour, as well as if the cancer has spread to other body parts.
- Stage 0 – The condition has no invasiveness. It indicates that it hasn’t emerged from your breast ducts.
- Stage I – The breast tissue has been infected with cancerous cells.
- Stage II – The tumour is either less than 2 centimetres in diameter and has spread to the underarm lymph nodes or more than 5 centimetres in diameter but has not migrated to the underarm lymph nodes. All in all, tumours at this stage can range in size from 2 to 5 centimetres in diameter and may or may not impact adjacent lymph nodes.
- Stage III – Cancer has already spread past its originating site in this stage. It could have expanded to neighbouring lymph nodes and tissue but hasn’t reached distant organs. Breast cancer at stage III is typically referred to as “locally progressed”.
- Stage IV – Your bones, liver, lungs, or brain are among the organs where cancer has metastasized outside your breast. Metastatic breast cancer is another name for Stage IV breast cancer.
What is the Treatment for Breast Cancer?
Chemotherapy, Surgery, Radiation therapy, & Hormone therapy are all possibilities for treating breast cancer. What is best for you is determined by a variety of criteria, including the location and size of the tumour, the results of your lab tests, and if cancer has progressed to other body parts.
To begin, your doctor will examine the size, stage, and spread of your cancer. Your healthcare practitioner will personalise your treatment strategy as per the individual diagnosis results and discuss the best options with you.
Surgery – Breast cancer can be removed using a variety of surgical procedures, including:
- Lumpectomy
- Mastectomy
- Sentinel node biopsy
- Axillary lymph node dissection
- Contralateral prophylactic mastectomy
Chemotherapy – To reduce the tumour before a lumpectomy, your doctor may consider chemotherapy. It is also sometimes administered after surgery to eliminate any leftover cancer cells and lower the chance of recurrence.
Radiation therapy – Radiation treatment uses high-powered radiation beams to target and kill cancer cells. Radiation therapy is prevalently used following a lumpectomy or mastectomy to eliminate any residual cancer cells.
Hormone therapy – If breast cancer is hormone-sensitive, your doctor may put you on hormone therapy. Hormone therapy either prevents your body from producing these hormones or inhibits the hormone receptors on cancer cells.
Breast Cancer – Is it Preventable?
Breast cancer cannot be entirely avoided. However, there are certain steps you may do to perhaps lower your chances of getting it. This can be particularly beneficial for women who have particular health risk factors for breast cancer, such as a family history or specific inherited gene alterations.
Keep Your Weight in Check – The chance of developing breast cancer post-menopause is raised by both increasing body weight and weight rise as an adult. Ask your doctor for advice on healthy weight loss methods if you need to lose some pounds.
Engage in some physical activity – It’s crucial to engage in routine physical activity since several research studies have found a correlation between moderate to intense physical activity and a decreased risk of breast cancer. You can avoid breast cancer by maintaining a healthy weight with the help of a physical activity.
Limit Your Alcohol Consumption – Your likelihood of getting breast cancer increases with the amount of alcohol you consume. Based on research, it is generally advised that if a woman drinks, she shouldn’t consume more than one alcoholic beverage every day.
Postmenopausal Hormone Treatment Should be Avoided – Chances of getting breast cancer may be increased by combination hormone treatment. If you want to eliminate this, discuss menopausal symptom treatment alternatives that aren’t hormonal with your healthcare physician.
Early Diagnosis of Breast Cancer
There are ways where you can readily detect or diagnose breast cancer at the early stages when it is not showing any symptoms. Here are a few ways you can follow.
- Self-breast examination by regularly checking your breasts for lumps or irregularities.
- Clinical Examination by visiting your doctor.
- Mammography where your doctor will do a screening test.
- Breast Ultrasound and Breast MRI are also effective ways for early detection of breast cancer.
- Lastly, if the above-mentioned methods are signalling a possibility of Breast Cancer, the doctor will have to do a Biopsy to confirm it.
To Conclude
It’s crucial to utilise the various services at your disposal despite the fact that getting a breast cancer diagnosis can seem frightening and upsetting for many. Your treatment strategy should make you happy and upbeat.