What is Rheumatology?
Rheumatology is a medical specialty focused on diagnosing and treating conditions affecting the musculoskeletal system, including joints, bones, muscles, and connective tissues. Rheumatologists specialize in managing autoimmune diseases, inflammatory conditions, and musculoskeletal pain disorders.
What conditions do Rheumatologists treat?
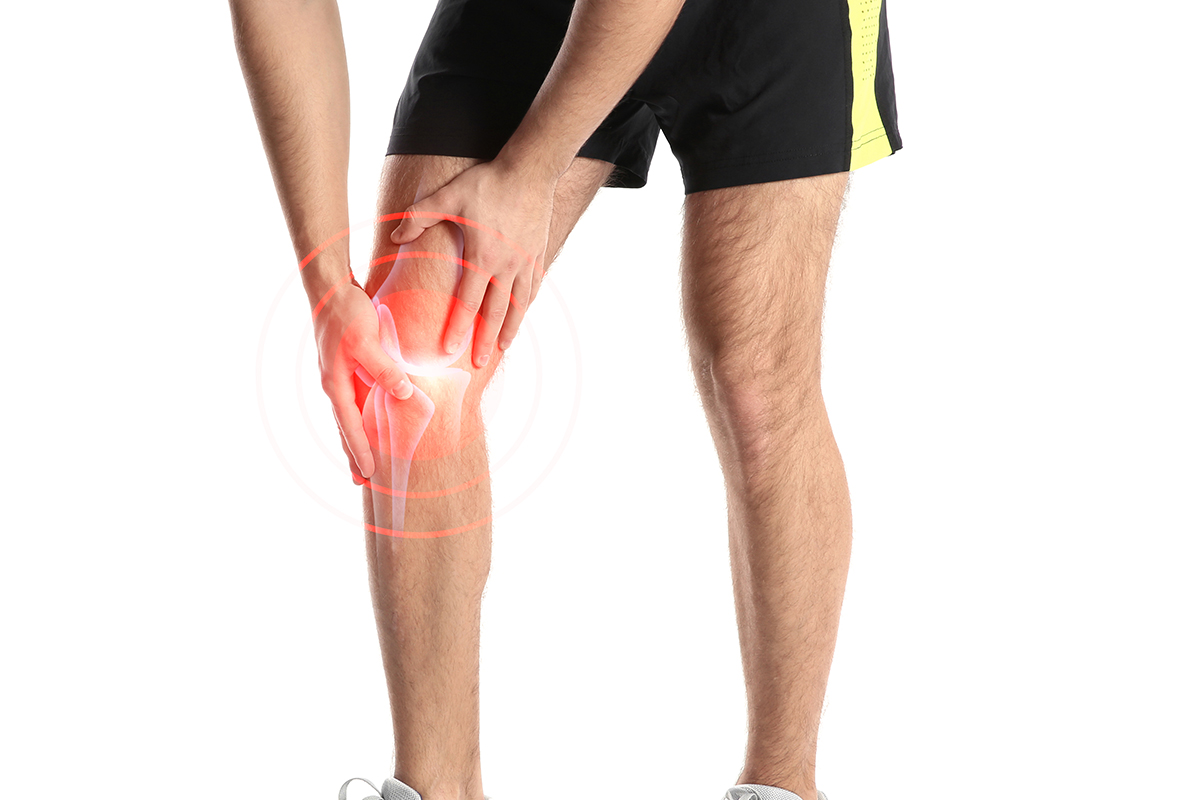
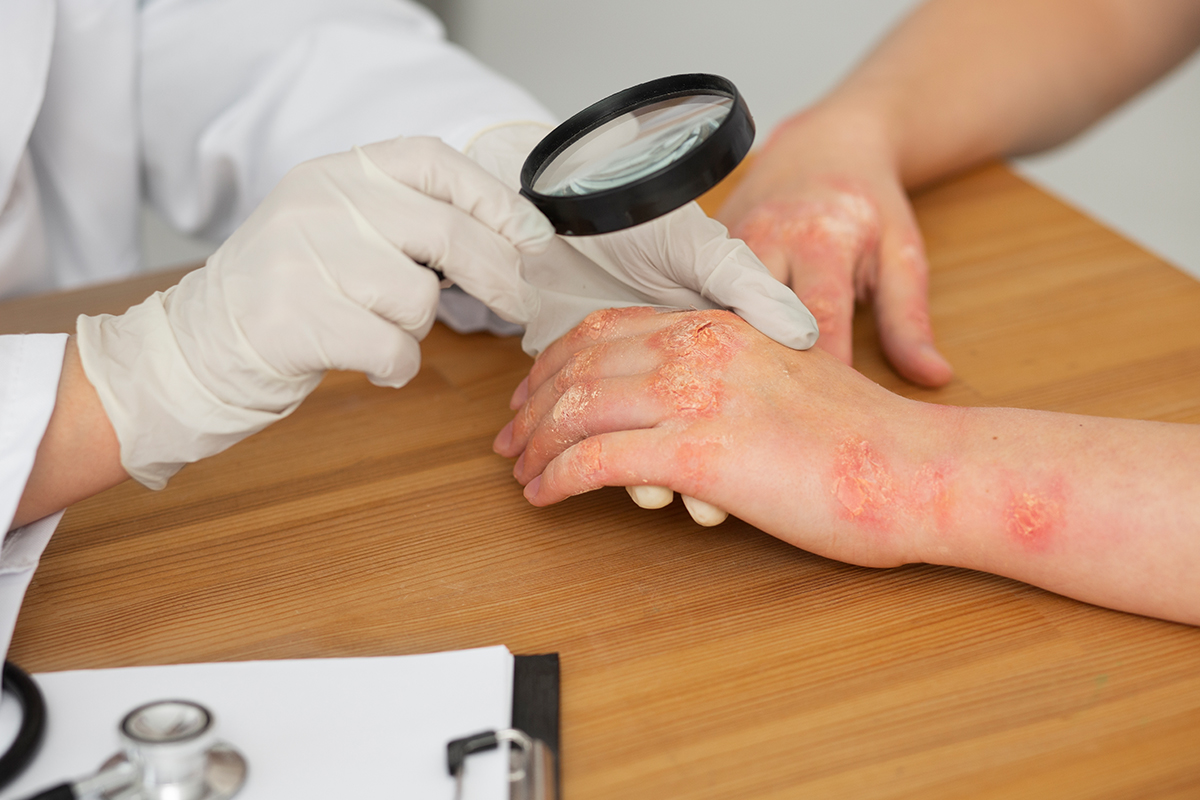
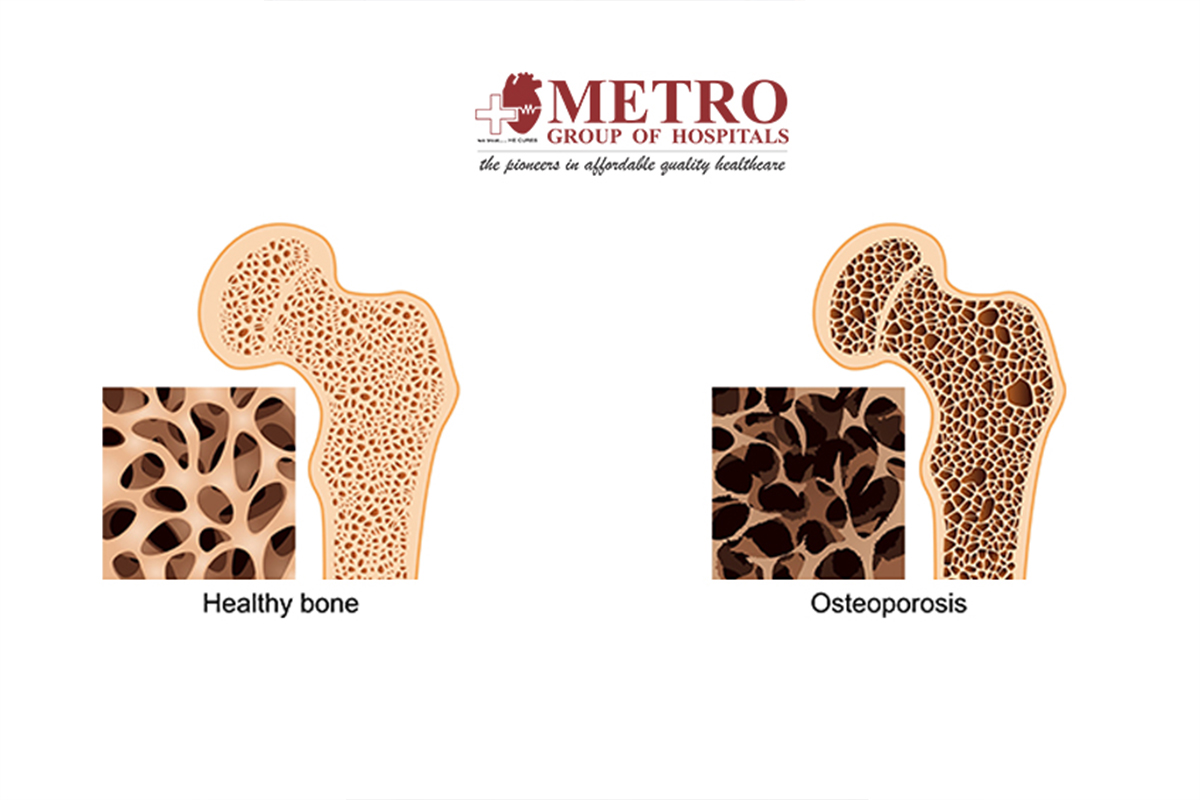
Rheumatologists treat a wide range of conditions, including rheumatoid arthritis, osteoarthritis, lupus, gout, fibromyalgia, osteoporosis, ankylosing spondylitis, and psoriatic arthritis, among others.
How do Rheumatologists differ from other doctors? Rheumatologists have specialized training in diagnosing and managing rheumatic diseases, which involve complex immune system responses and chronic inflammation. They are experts in recognizing the signs and symptoms of these conditions and developing personalized treatment plans.
When should I see a Rheumatologist? You should consider seeing a rheumatologist if you experience persistent joint pain, stiffness, swelling, or other symptoms suggestive of a rheumatic condition. Additionally, if you have been diagnosed with an autoimmune disease or inflammatory arthritis, a rheumatologist can provide specialized care and management.
What can I expect during a Rheumatology appointment? During a rheumatology appointment, the rheumatologist will perform a thorough evaluation, which may include a review of your medical history, physical examination, and possibly diagnostic tests such as blood tests, imaging studies, or joint aspiration. Based on the findings, the rheumatologist will discuss your diagnosis and develop a treatment plan tailored to your needs.
What treatments do Rheumatologists offer? Rheumatologists may recommend a variety of treatments depending on the specific condition and its severity. Treatment options may include medications (such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs, biologic agents), physical therapy, lifestyle modifications, and other interventions to manage symptoms and improve quality of life.
Here are some common diseases treated by rheumatologists
- Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA): RA is an autoimmune disorder characterized by chronic inflammation of the joints, leading to pain, swelling, stiffness, and eventually joint damage and deformity. Rheumatologists help manage RA through medications, lifestyle modifications, and interventions to alleviate symptoms and prevent disease progression.
- Osteoarthritis (OA): OA is a degenerative joint disease characterized by the breakdown of cartilage in the joints, leading to pain, stiffness, and reduced mobility. Rheumatologists provide treatments such as pain management, physical therapy, and joint injections to relieve OA symptoms and improve joint function.
- Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE): SLE is a chronic autoimmune disease that can affect various organs and tissues in the body, including the skin, joints, kidneys, and heart. Rheumatologists manage SLE through medications to control inflammation, minimize organ damage, and improve quality of life.
- Ankylosing Spondylitis (AS): AS is a type of inflammatory arthritis that primarily affects the spine, causing pain, stiffness, and reduced flexibility. Rheumatologists prescribe medications, physical therapy, and lifestyle modifications to manage AS symptoms and prevent complications.
- Sjögren’s Syndrome: Sjögren’s syndrome is an autoimmune disorder characterized by dryness of the eyes and mouth, as well as fatigue and joint pain. Rheumatologists help manage Sjögren’s syndrome through medications to alleviate symptoms and prevent complications such as eye damage and dental problems.
- Psoriatic Arthritis (PsA): PsA is a type of inflammatory arthritis that affects some people with psoriasis, causing joint pain, swelling, and stiffness, along with skin symptoms. Rheumatologists provide treatments to reduce inflammation, relieve pain, and slow down joint damage in PsA patients.
- Gout: Gout is a type of arthritis caused by the buildup of uric acid crystals in the joints, leading to sudden and severe pain, swelling, and redness. Rheumatologists help manage gout through medications to lower uric acid levels, reduce inflammation, and prevent recurrent attacks.
- Fibromyalgia: Fibromyalgia is a chronic pain disorder characterized by widespread musculoskeletal pain, fatigue, sleep disturbances, and cognitive difficulties. Rheumatologists work with patients to develop personalized treatment plans that may include medications, exercise, stress management techniques, and cognitive behavioral therapy.
- Vasculitis: Vasculitis is a group of rare autoimmune diseases characterized by inflammation of blood vessels, which can affect various organs and tissues in the body. Rheumatologists diagnose and treat vasculitis using medications to suppress inflammation and prevent organ damage.
- Behçet’s Disease: Behçet’s disease is a rare autoimmune disorder that causes inflammation of blood vessels throughout the body, leading to recurrent mouth and genital ulcers, skin lesions, eye inflammation, and joint pain. Rheumatologists manage Behçet’s disease through medications to control inflammation and alleviate symptoms.
Can Rheumatic diseases be cured? While many rheumatic diseases are chronic and do not have a cure, rheumatologists can help manage symptoms, slow disease progression, and improve quality of life through appropriate treatment and ongoing monitoring.
What lifestyle changes can help manage Rheumatic conditions? Rheumatologists may recommend lifestyle modifications such as regular exercise, maintaining a healthy weight, managing stress, getting adequate rest, and following a balanced diet rich in anti-inflammatory foods to help manage rheumatic conditions.
Are there any new advancements in Rheumatology treatment? Yes, there have been significant advancements in rheumatology treatment in recent years, including the development of targeted biologic therapies, personalized medicine approaches, and novel treatment strategies aimed at improving outcomes and reducing side effects.